Parts List
Friend
Find methods for your needs
TN121: Fast Determinations of Inorganic Cations in Municipal Wastewater Using High-Pressure Capillary IC
Description
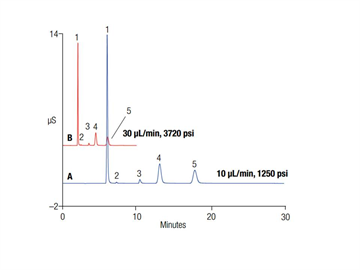
Inorganic cations were determined in municipal wastewater samples using a high pressure capillary IC system. All six cations were separated on IonPac CS16 capillary column at 30 mM MSA and 40 C. The high pressure capabilities of the ICS-5000+ capillary IC system were demonstrated by using flow rates at 3x of the typical capillary flow rate, 30 uL/min. The separation at the standard flow rate of 10 uL/min is also shown. An ICS-6000 can be used for this application.| Market: | Environmental |
| Keywords: | Magnesium, waste water, Lithium, RFIC, Potassium, IonPac CS16 column, cap IC, IC, Calcium, Sodium, capillary IC, wastewater, Ammonium, cations, ICS-6000 |
| Matrix: | Municipal wastewater |
| Author: | Terri Christison, Fei Pang, and Linda Lopez |
| Affiliation: | Thermo Fisher Scientific |
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.