Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-5 of 7 results for Tag: power plant
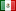
AN1145: Determination of Halogens in Coal Using Combustion Ion Chromatography
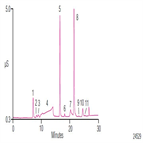
Instrument Type: ICWhen coal is burned, the exhaust contains halogens that can be released into the atmosphere as acid gases such as hydrogen chloride (HCl) and hydrogen fluoride (HF), which can harm vegetation, animals, and infrastructure directly or cause acid rain. In this application note, coal samples were combusted in the Mitsubishi AQF-2100H system and then fluorine and chlorine were accurately and precisely determined using the Dionex ICS-2100 Ion Chromatography System with a Dionex IonPac AS15 anion-exchange column set.
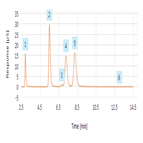
Determination of Chlorine and Sulfur in Wood Chips Using Combustion Ion Chromatography
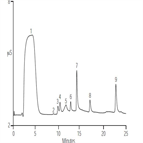
Instrument Type: ICWood chips are used for producing paper and are also contained in waste deposits. It is important to know the halogen contents of wood chips for impurity management in paper production and for environmental assessment in waste materials. By using a combustion ion chromatography (CIC) system consisting of the automatic quick furnace AQF-2100H and an ICS-1600 ion chromatograph, the concentrations of halogens and sulfur can be determined accurately and quickly.
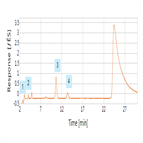
Determination of Halogens and Sulfur in Refuse Derived Fuel by Combustion Ion Chromatography
Instrument Type: ICRefuse Derived Fuel (RDF) is a fuel produced by shredding and dehydrating solid waste deriving largely from municipal waste. Because RDF is used as fuel for power plants and boilers, it is important to know the halogen and sulfur content as an indication of the potential for formation of corrosives or environmental contaminants. By using a combustion ion chromatography (CIC) system consisting of the automatic quick furnace AQF-2100H and an ICS-1600 ion chromatograph, the concentrations of halogens and sulfur can be determined accurately and quickly.
AN185: Determination of Trace Organic Acids and Inorganic Anions in Boric Acid-Treated Power Plant Waters Using an Automated Reagent-Free Ion Chromatography System
Instrument Type: ICBoron as boric acid is used to control the nuclear reaction in pressurized water reactors because of its strong neutron-absorbing characteristics. To prevent corrosion, anionic contamination is monitored. Here sub-ppb concentrations of inorganic anions in a large volume sample are determined in borated waters using matrix elimination through the use of a CR-CTC trap column. The anions were collected on a concentrator column, eluted and determined using an electrolytically generated hydroxide gradient on IonPac AS15 column. This is an improvement over using borated eluents (AN166).
AN166: Application of Eluent Generation for Trace AnionAnalysis of Borated Waters
Instrument Type: ICBoron as boric acid is used to control the nuclear reaction in pressurized water reactors because of its strong neutron-absorbing characteristics. To prevent corrosion, anionic contamination is monitored. Here sub-ppb concentrations of inorganic anions are determined in borated waters (<7500 mg/L boron) by large volume, direct injection using a tetraborate gradient on IonPac AS14 column. The tetraborate eluent is automatically generated inline by titrating 50 mM boric acid with electrolytically generated KOH. This is an improvement over using manually prepared solutions (AU102, AU191).