Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-4 of 4 results for Tag: Plant
AN350: Extraction of Zearalenone from Wheat and Corn by Accelerated Solvent Extraction (ASE)
Instrument Type: Automated Sample PrepZearalenone (ZON) is a mycotoxin produced by the Fusarium fungus. ZON can be found in a wide variety of plants and soils, and can have negative health effects on animal husbandry and humans. Accelerated Solvent Extraction (ASE) is a proven extraction technology that not only helps to eliminate these bottlenecks by decreasing the extraction time, but requires far less technician attendance because it is an automated system.
AN357: Extraction of Phenolic Acids from Plant Tissue Using Accelerated Solvent Extraction (ASE)
Instrument Type: Automated Sample PrepThis application note will focus on the extraction of phenolic acids from two different plants (eggplants and black cohosh) using ASE. The ASE results from five different eggplant samples are compared to eight different extraction techniques. Data from the extraction of black cohosh show the results of the optimum ASE conditions for this matrix, focusing on temperature and solvent choice.
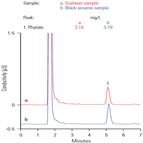
AN295: Determination of Phytic Acid in Soybeans and Black Sesame Seeds
Instrument Type: ICPhytic acid is the storage form of phosphate in many plant tissues, especially seeds and grains. Because phytic acid is a good metal chelator, it is believed to have a negative nutritional impact on strongly chelating metals necessary for good health. The method reported here uses the hydroxide-selective Dionex IonPac AS11 column to separate phytate from other anions (including the remaining chloride from the sample preparation) with an isocratic method.
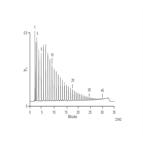
AU150: Determination of Plant-Derived Neutral Oligo- and Polysaccharides
Instrument Type: ICSince the publication of Application Note 67, Dionex introduced the Dionex CarboPac™ PA200, a column designed for even higher-resolution separations than the Dionex CarboPac PA1 or PA100 columns. The improved resolution is due in part to the PA200’s significantly smaller substrate (5.5 μm) and latex (43 nm) beads. These and other changes produce a column that has greater resolution and requires a lower sodium acetate concentration to elute a given oligosaccharide than the PA100. The AU highlights the benefits of the PA200 for these applications.