Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-5 of 6 results for Tag: Cytochrome C
High-precision, automated peptide mapping of proteins
Instrument Type: UHPLCThe biopharmaceutical industry continues to develop protein-based biotherapeutics in increasing numbers. Due to their complexity and biotechnological production, there are many attributes that need to be analyzed to guarantee their safety and efficacy. Peptide mapping is used to measure several critical quality attributes (CQA) required for the characterization of any biotherapeutic protein. The analysis is used to confirm that the correct sequence has been expressed for the protein and to check for post-translational and chemical modifications.
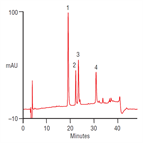
Simple gradient method for the analysis of protein standards by micro LC
Instrument Type: HPLCThe Thermo Scientific HPLC system is applied for the analysis of protein standards. The separation is performed on a Thermo Scientific Acclaim 300 C18 micro LC column, with UV detection at 214 nm.
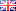
High resolution separation of Cytochrome C tryptic peptides
Instrument Type: HPLCThe Thermo Scientific HPLC system is applied for the analysis of Cytochrome C tryptic peptides. The separation is performed using a Thermo Scientific Acclaim 300 C18 column, with UV detection at 214 nm.
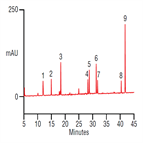
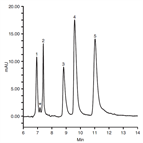
High resolution separation of Cytochrome C from three different species
Instrument Type: HPLCThe Thermo Scientific HPLC system is applied for the analysis of Cytochrome C from three different species (yeast, equine and bovine). The separation is performed using a Thermo Scientific Acclaim 300 C18 column, with UV detection at 214 nm.
Improved analysis of intact proteins using a Thermo Scientific Accucore 150-C4 150 Å pore diameter nanoLC column
Instrument Type: HPLCThe Thermo Scientific HPLC system is applied for the analysis of intact proteins (*indicates an impurity from carbonic anhydrase). The separation is performed on a Thermo Scientific Accucore 150-C4 150 Å pore diameter nanoLC column, with UV detection at 214 nm. The 150 Å pore size enables the effective analysis of molecules unable to penetrate into smaller diameter pores, whilst the low hydrophobicity C4 phase results in protein separation by hydrophobicity.