Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-4 of 4 results for Tag: Copper plating
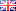
AU143: Determination of Chloride in Acid Copper Plating Bath
Instrument Type: ICIon chromatography provides a convenient method for the determination of chloride in acid copper plating baths. Monitoring chloride concentration is of interest because it plays an important role in the quality of copper deposition. Compared to standard wet chemical techniques, IC offers improved speed and accuracy for this analysis. Chloride is separated from the excess of sulfate present in the copper plating bath. Chloride is detected by suppressed conductivity and the EG40 eluent generator is used to prepare the 30 mM potassium hydroxide eluent on-line.
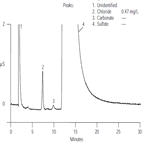
AN55: Determination of Metal Cyanides
Instrument Type: ICTransition metal cyanides typically exist in solution as the anionic cyanometallates, M (CN)x^n-. Since these complexes are very stable (formation constants being as high as 10^35 for Fe (CN)6^4-), they may be separated by anion exchange chromatography. Cyano complexes of most of the transition metals absorb low-wavelength ultraviolet light, making detection at 215 nm a convenient method of determination. Also refer to AN161 and AU147 for an updated method.
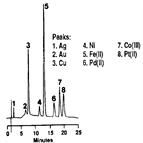
AN145: Determination of the Suppressor Additive in Acid Copper Plating Bath
Instrument Type: HPLCCopper electroplating systems are used for the deposition of copper on semiconductor wafers. A proprietary suppressor additive is used to influence the quality of copper deposition. Because maintaining the level of the suppressor within the recommended operating range ensures the quality of the fill, we developed a method to determine the suppressor additive. This application note describes the use of the IonPac NS1 column with evaporative light-scattering detection to determine two different proprietary suppressors in acid copper plating baths.
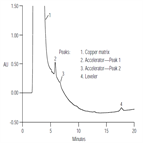
AN139: Determination of Additives and Byproducts in an Acid Copper Plating Bath by Liquid Chromatography.
Instrument Type: HPLCCopper electroplating systems are used for the deposition of copper on semiconductor wafers. The primary components of an acid copper plating bath are copper sulfate, sulfuric acid, and hydrochloric acid. As the bath ages, certain byproducts are formed as a result of the plating process. Tracking the levels of these components ensures the quality of the fill. Chromatography can be used to quantitatively measure individual components. This Application Note describes the use of the IonPac NS1 column with absorbance detection to determine additives and byproducts in acid copper plating baths.