Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-4 of 4 results for Tag: boron
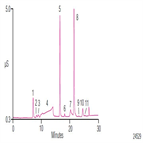
AU175: Determination of Organic Acids and Inorganic Anions in Lithium-Containing Boric Acid-Treated Nuclear Power Plant Waters
Instrument Type: ICIn nuclear power plants with pressurized water reactors the primary coolant includes boric acid, which at high temperature and pressure can form crud. Lithium hydroxide is added to prevent this. Trace anionic impurities can serve as catalysts for corrosion. The experimental approach shown in this work combines the direct injection, electrolytically generated tetraborate eluent approach to analyze lithium-containing borated waters for fluoride, formate, chloride, and sulfate with the addition of a continuously regenerated cation trap column to remove lithium and other cations from the sample.
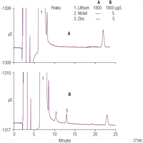
AN250: Determination of Trace Nickel and Zinc in Borated Power Plant Waters Containing Lithium Hydroxide Using Nonsuppressed Conductivity Detection
Instrument Type: ICBoron as boric acid is used to control the nuclear reaction in pressurized water reactors (PWR) because of its strong neutron-absorbing characteristics. In addition, lithium is added to adjust the pH and zinc is added to suppress cobalt (58Co, 60Co) activity. Dissolved Ni in these solutions can be indicator of stress corrosion. To minimize corrosion, Ni and Zn monitoring is needed. Here µg/L of Ni and Zn in borated lithium water samples are determined on IonPac SCS-1 column and detected by non-suppressed conductivity. We recommend AN277 if sub-ppb detection is needed.
AN185: Determination of Trace Organic Acids and Inorganic Anions in Boric Acid-Treated Power Plant Waters Using an Automated Reagent-Free Ion Chromatography System
Instrument Type: ICBoron as boric acid is used to control the nuclear reaction in pressurized water reactors because of its strong neutron-absorbing characteristics. To prevent corrosion, anionic contamination is monitored. Here sub-ppb concentrations of inorganic anions in a large volume sample are determined in borated waters using matrix elimination through the use of a CR-CTC trap column. The anions were collected on a concentrator column, eluted and determined using an electrolytically generated hydroxide gradient on IonPac AS15 column. This is an improvement over using borated eluents (AN166).
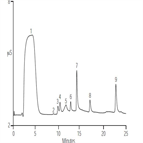
AN166: Application of Eluent Generation for Trace AnionAnalysis of Borated Waters
Instrument Type: ICBoron as boric acid is used to control the nuclear reaction in pressurized water reactors because of its strong neutron-absorbing characteristics. To prevent corrosion, anionic contamination is monitored. Here sub-ppb concentrations of inorganic anions are determined in borated waters (<7500 mg/L boron) by large volume, direct injection using a tetraborate gradient on IonPac AS14 column. The tetraborate eluent is automatically generated inline by titrating 50 mM boric acid with electrolytically generated KOH. This is an improvement over using manually prepared solutions (AU102, AU191).