Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-4 of 4 results for Tag: Sugar Phosphate
CAN109: Primary Metabolite Analysis of Plant Material Using a Triple Quadrupole MS Coupled to a Monolith Anion-Exchange Column
Instrument Type: ICMSA platform using Dionex ion chromatography (IC) coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (MS) was developed to measure various metabolites in Brassica napus seeds. The IC tandem mass spectrometry (IC-MS/MS) technique provides a good tool to identify and quantify metabolites in a complex matrix.
CAN108: Ion Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry for Metabolomics
Instrument Type: ICMSHere, the author describes an ion-exchange system that provides good separation of the polar metabolities with on-line desalting to allow MS detection. This technique will allow studies of key metabolites that do not separate well on traditional reversed-phase columns. Some ionic metabolites may be positional isomers adjacent to each other in a synthetic pathway and as such, are isobaric. In such cases, MS is not sufficient to differentiate the two compounds. There is clearly a need for adequate separation techniques for isomeric metabolites.
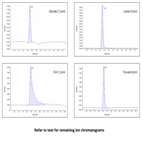
AN215: Separation of Asparagine-Linked (N-Linked) Oligosaccharides from Human Polyclonal IgG
Instrument Type: ICThis application note shows how the PA200 improves N-linked oligosaccharide separations. The PA200 is used to profile N-linked oligosaccharides released from human polyclonal IgG by the enzyme PNGase F or endoglycosidase H (Endo H). This note also shows how subsequent exoglycosidase digestions can be used to assist in understanding and identifying oligosaccharide structure.
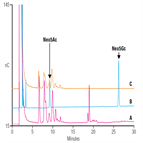
Fast analysis of sugar phosphates by HPLC-CAD
Instrument Type: HPLC-CADThe Thermo Scientific UltiMate 3000RS system is applied for the analysis of sugar phosphates. The separation is performed using a Thermo Scientific GlycanPac AXH-1 1.9µm column, with charged aerosol detection. The Thermo Scientific GlycanPac AXH-1 is a column designed to classify anionic carbohydrates by charge and resolve them by HILIC interactions. For this group of simple sugar phosphates, an isocratic analysis is sufficient using a volatile mobile phase that is compatible with charged aerosol detection or mass spectrometry.