Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-5 of 11 results for Tag: Polychlorinated biphenyl
AN352: Rapid Determination of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) Using Accelerated Solvent Extraction (ASE)
Instrument Type: Automated Sample PrepThe following compounds are listed by UNEP to be POPS: • Pesticides: Aldrin, Chlordane, DDT, Dieldrin, Endrin, Heptachlor, Mirex, and Toxaphene • Industrial chemicals: Hexachlorobenzene, and PCB (polychlorinated biphenyl) • Chemical by-products (Dioxins): Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDD and PCDF) This application note describes methods and results for extraction of the POPs listed above, with tables comparing ASE to traditional extraction methods.
AN337: Extraction of Lipids and Polychlorinated Biphenyls from Fish Tissue in a Single Run Using Accelerated Solvent Extraction (ASE)
Instrument Type: Automated Sample PrepASE is an automated extraction technique that uses traditional liquid solvents at elevated pressure and temperature. The extraction is performed at temperatures higher than the atmospheric pressure boiling point of the solvent. High temperature substantially increases solvation kinetics and the high pressure ensures that the solvent remains a liquid. This application note provides full details of the extraction parameters and a comparison of ASE and Soxhlet extraction results.
AN1025: Simultaneous Extraction of PAHs and PCBs from Environmental Samples Using Accelerated Solvent Extraction
Instrument Type: Automated Sample PrepAccelerated solvent extraction is an established technique to efficiently extract contaminants in solid and semisolid sample matrices with less solvent and time. Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) are considered toxic and carcinogenic, and therefore classified as persistent organic pollutants (POPs). Typically, PAHs and PCBs are extracted separately, using different solvent combinations. Our study demonstrates extraction of PAHs and PCBs using a single method from spiked mussel and from a soil spiked with a standard reference materials (SRMs).
AN342: Determination of PCBs in Large-Volume Fish Tissue Samples Using Accelerated Solvent Extraction (ASE)
Instrument Type: Automated Sample PrepPCBs are a persistent organic pollutant (POP) and therefore are monitored in marine life including fish. Automated Solvent Extraction (ASE 350) technology, an automated extraction method, has been shown to produce good recoveries of naturally occurring PCBs from fish tissue samples, and is approved for use in U.S. EPA SW-846 Method 3545 for the extraction of PCBs, OCPs, BNAs, OPPs, herbicides, and dioxins and furans. ASE operates at elevated temperatures, thus increasing the efficiency of the extraction process. Here we demonstrate the extraction of PCBs in a raw fish tissue sample.
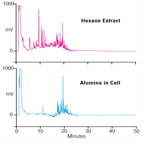
AN322: Selective Extraction of PCBs from Fish Tissue Using Accelerated Solvent Extraction
Instrument Type: Automated Sample PrepThe analysis of extracts containing polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) contaminants from fish tissue and fish homogenates can be hindered by the presence of coextracted fatty materials. Here demonstrates that selective extractions can be performed using accelerated solvent extraction with the proper choice of solvent and sorbent in the extraction cell. Results are given for the recovery of PCBs from contaminated fish tissue showing that extracts do not require further cleanup prior to analysis by gas chromatography when using accelerated solvent extraction.