Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-5 of 5 results for Tag: Glucocorticoid
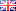
Simplified, high-throughput separation of glucocorticoids
Instrument Type: UHPLCImproved separation of closely related glucocorticoids with reduced method complexity High-throughput analysis possible through a reduced complexity, rapid, two-minute isocratic method Associated reduction in cost per sample through reduced mobile phase consumption and waste generation
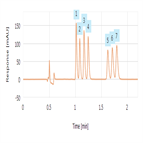
Detection of Glucocorticoid Residues in Animal-derived Food by HPLC-MS/MS
Instrument Type: LCMSMSWe developed an effective LC-MS/MS method to detect eight gluococorticoid residues in the liver and muscles of pig, cattle, and lamb, as well as in chicken, eggs and milk.
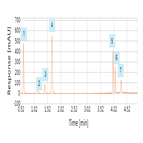
Reproducible separation of acidic and neutral drugs using a solid core C18 HPLC column
Instrument Type: HPLCThe separation of acidic and neutral drugs was successfully achieved on the Thermo Scientific Accucore C18 column, providing an excellent choice for the analysis of these drugs giving excellent retention time reproducibility and resolution.
Improved isocratic separation of basic, neutral, and acidic molecules on a Thermo Scientific Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX-1 column
Instrument Type: HPLCThe Thermo Scientific Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX-1 column is used for the isocratic separation of basic, neutral and acidic pharmaceuticals.The novel column chemistry of the Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX-1 column provides a multi-mode separation mechanism that includes hydrophobic, anion-exchange and cation-exclusion interactions.
Improved gradient separation of basic, neutral, and acidic pharmaceuticals on a Thermo Scientific Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX-1 HPLC column
Instrument Type: HPLCThe Thermo Scientific Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX-1 column is used for the gradient separation of basic, neutral and acidic pharmaceuticals.The novel column chemistry of the Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX-1 column provides a multi-mode separation mechanism that includes hydrophobic, anion-exchange and cation-exclusion interactions.