Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-5 of 5 results for Tag: QA/QC
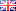
A rapid fenoprofen USP assay method
Instrument Type: UHPLCFive-fold increase in method throughput compared to original method (fifty samples/hour). Associated 10-fold reduction in cost per sample through reduced mobile phase consumption and waste generation. Additional reduced method complexity from easy-to-prepare mobile phase
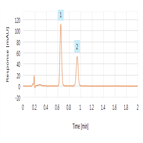
Simplified, high-throughput separation of glucocorticoids
Instrument Type: UHPLCImproved separation of closely related glucocorticoids with reduced method complexity High-throughput analysis possible through a reduced complexity, rapid, two-minute isocratic method Associated reduction in cost per sample through reduced mobile phase consumption and waste generation
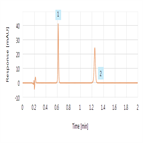
A rapid cephradine USP assay method
Instrument Type: UHPLCTo demonstrate practical approaches that can be used to significantly improve throughput of the cephradine USP assay monograph keeping to the spirit of USP-NF Chapter <621> guidelines while maintaining USP quality acceptance criteria.
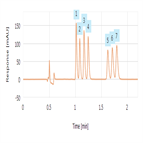
A rapid ibuprofen USP assay method
Instrument Type: UHPLCTo demonstrate practical approaches that can be used to significantly improve throughput of the ibuprofen USP assay monograph keeping to the spirit o USP-NF Chapter <621> guidelines while maintaining USP quality acceptance criteria. To then take this optimized assay monograph and reduce analysis time even further.
High-precision, automated peptide mapping of proteins
Instrument Type: UHPLCThe biopharmaceutical industry continues to develop protein-based biotherapeutics in increasing numbers. Due to their complexity and biotechnological production, there are many attributes that need to be analyzed to guarantee their safety and efficacy. Peptide mapping is used to measure several critical quality attributes (CQA) required for the characterization of any biotherapeutic protein. The analysis is used to confirm that the correct sequence has been expressed for the protein and to check for post-translational and chemical modifications.