Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-3 of 3 results for Tag: NMP
AN85: Determination of Trace Anions in (N-Methylpyrrolidone) Organic Solvents
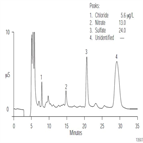
Instrument Type: ICThe determination of trace anionic contamination in processing solvents (N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), isopropyl alcohol, and acetone) is important to the electronics industries to minimize corrosion. Here matrix elimination is used to retain and concentrate µg/L anionic contamination in a 5 mL NMP sample onto a concentrator column. NMP is flushed to waste (5 min) with purified deionized water (10 mL). Trace anions are eluted from the concentrator and separated on IonPac AS9-HC column using 8 mM carbonate, 1.5 mM NaOH eluent. AU163 updates AN85 with < 0.2 ug/L lower detection limits.
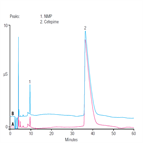
AN259: Determination of N-Methylpyrrolidine in Cefepime with Nonsuppressed Conductivity Detection
Instrument Type: ICThis work describes the determination of N-Methylpyrrolidine by cation-exchange chromatography with non-suppressed conductivity detection. This method is different from the one described in AN199, which uses suppressed conductivity. The results shown here meet the USP criteria for Organic Impurities, Procedure 1 (Limit of N-Methylpyrrolidine) in the proposed methods for cefepime hydrochloride and Cefepime for Injection.
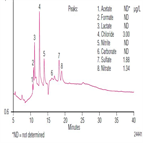
AU163: Determination of Trace Anions in Organic Solvents Using Matrix Elimination and Preconcentration
Instrument Type: ICAnion contamination introduced during manufacturing processes can ruin semiconductor devices, and therefore trace contaminants in solvents are a concern. This method successfully determines trace anions (high ng/L to low μg/L) in isopropyl alcohol, methanol, acetone, and n-methyl-2-pyrrolidone by matrix elimination. Results show improved method detection limits (MDLs) using 60% smaller sample injections. The method easily meets the Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International (SEMI®) specifications for solvents, with typically 100- to 2800-fold lower MDLs than the SEMI specifications.