Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-5 of 7 results for Tag: Fruit juice
AB137: Determination of Inorganic and Organic Acids in Apple and Orange Juice Samples Using Capillary IC
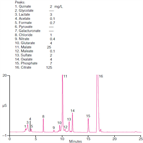
Instrument Type: ICDeterminations of organic acids in fruit juices are used by the beverage industry for flavor characterization, identification of spoilage, identification of adulteration by a less costly juice, and product labeling. In this study, inorganic anions and organic acids in diluted filtered apple and orange juice samples were determined on a Dionex IonSwift MAX-100 anion-exchange column using electrolytically generated hydroxide gradient from 0.1–65 mM KOH over 25 min at 15 μL/min.
AB117: Determination of Cations in Fruit Juices
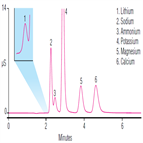
Instrument Type: ICDetermining cations, such as potassium, sodium, and calcium, in fruit juices is important due to the dietary significance of such cations. A simple Ion chromatography (IC) method to determine cations in fruit juices requires only a 1:100 dilution followed by injection. This method use 2 mm diameter IonPac CS12A column and provides results for multiple ions in a 5 min analysis.
AB127: Determination of Carbohydrates in Fruit Juice Using Capillary High-Performance Anion-Exchange Chromatography
Instrument Type: ICWhen using high-performance anion-exchange chromatography (HPAE) coupled with pulsed amperometric detection (PAD) for carbohydrate analysis, scaling down from analytical to a capillary scale system provides many benefits. These include the fact that the system can be left on and ready to run samples, and the capillary eluent generation cartridge (EGC) produces ultrapure carbonate-free potassium hydroxide eluent up to 200 mM and lasts 18 months. This application demonstrates determination of glucose, fructose, and sucrose in fruit juices using a Dionex CarboPac PA20 column in capillary format.
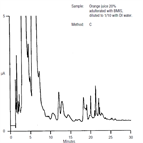
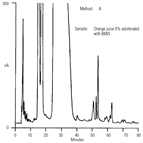
AN82: Analysis of Fruit Juices Adulterated with Medium Invert Sugar from Beets (Method C)
Instrument Type: ICFruit juice adulteration presents an economic & regulatory problem. Investigators using high performance anion exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection(HPAE-PAD) discovered several components in beet medium invert sugar(BMIS) that are not present in orange juice. The selectivity of anion-exchange chromatography, especially for oligosaccharides, the sensitivity and specificity of pulsed amperometric detection make HPAE-PAD uniquely suited to this analysis. Today we would use a different electrochemical waveform (see TN21) and post-column addition of NaOH would not be required.
AN82: Analysis of Fruit Juices Adulterated with Medium Invert Sugar from Beets (Method A)
Instrument Type: ICFruit juice adulteration presents an economic & regulatory problem. Investigators using high performance anion exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection (HPAE-PAD) have discovered several components in beet medium invert sugar (BMIS) that are not present in orange juice. The selectivity of anion-exchange chromatography, for oligosaccharides, and the sensitivity and specificity of pulsed amperometric detection make HPAE-PAD uniquely suited to this analysis. Today we would use a different electrochemical waveform (see TN21) and post-column addition of NaOH would not be required.