Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-2 of 2 results for Tag: Dermatan sulfate
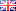
AU178: A Faster Solution with Increased Resolution for Determining Chromatographic Identity and Absence of OSCS in Heparin Sodium
Instrument Type: ICHere, an improved method for resolving DS and OSCS in heparin with an IonPac AS11-HC (2 × 250 mm) column is demonstrated, which is similar to the US FDA method previously described. AU178 updates Application Note 235. The higher capacity of the IonPac AS11-HC column, relative to the IonPac AS11 column described in the current USP method, minimizes the possibility of column overload and provides improved resolution between DS and heparin. The microbore column format reduces eluent consumption and hence the time and labor required for manual eluent preparation.
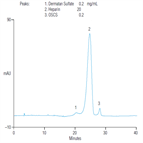
AN235: Determination of Oversulfated Chondroitin Sulfate and Dermatan Sulfate in Heparin Sodium Using Anion-Exchange Chromatography with UV Detection
Instrument Type: ICHeparin, a complex sulfated glycosaminoglycan, is a well-known anticoagulant used to stop or prevent blood from clotting in certain types of surgeries and dialysis treatments. In 2008, a galactosamine-based synthetic contaminant, called Oversulfated Chondrotin Sulfate (OSCS), was identified in Heparin as causing severe adverse affects and in some, death. The current USP 32 monograph from 2008 was upgraded to include chromatographic methods to detect OSCS and the natural contaminant, dermatan sulfate (DS). In this method, heparin, DS, and OSCS were separated by IC and detected at 202 nm.