Parts List
Friend
Find methods for your needs
AN173: Direct Determination of Cyanide in Drinking Water by Ion Chromatography with Pulsed Amperometric Detection (PAD)
Description
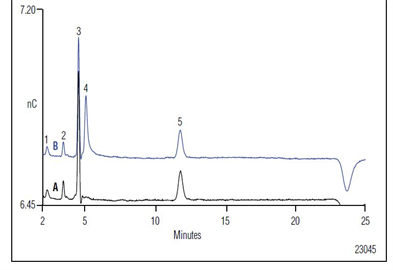
Cyanide, a well known acute toxin, occurs both naturally and as an industrial contaminant. In the U.S., cyanide contamination in drinking water is typically from an industrial source or leached from waste sites. In EPA Method 335, samples are individually acid- or UV-digested to convert all cyanide compounds to hydrogen cyanide gas which is distilled into sodium hydroxide (pH 13). These high pH matrixes can cause interferences in spectrophotometric methods. Here free cyanide is separated by IC and detected electrochemically using Ag working electrode and waveform for cyanide determinations.| Market: | Environmental |
| Keywords: | Electrochemical detection, IC-PAD, Pulsed Amperometric Detection, Ag working electrode, cyanide, free cyanide, PAD, surface water, Drinking water, AN173, AN 173, AN 227, AN227, total cyanide, AN 71020, AN71020 |
| Matrix: | Surface water |
| Author: | Terri Christison and Jeff Rohrer |
| Affiliation: | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA USA |
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.