Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-5 of 6 results for Tag: speciation
TN26: Determination of Cr(VI) in Water, Wastewater, and Solid Waste Extracts
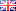
Instrument Type: ICThe method presented here overcomes analyte interference by separating the two chromium using a detection method specific for Cr(VI) that is capable of handling the high-ionic-strength sample matrices generated in many leaching, and digestion procedures. Cr(VI) is separated as the divalent anion on the IonPac AS7 column using ammonium sulfate, ammonium hydroxide eluent. After the separation, Cr(VI) reacts with the color reagent diphenylcarbohydrazide (DPC) and detected by UV absorbance at 520 nm. This method is consistent with U.S. EPA Method 218.6. Please refer to AU179 for an updated method.
AN43130: Combining the Synergies of Ion Chromatography and Inductively Coupled Plasma to Identify Mercury Contamination in Herbal Medicines
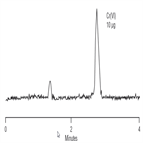
Instrument Type: ICHerbal medicines containing high total mercury concentrations were previously identified (ICP-MS) as the possible cause of several cases of accidental mercury poisoning. Because mercury species have very different toxicities, speciation analysis is needed to determine the patients’ treatment. Here inorganic and organic mercury ions are separated by IC using a mixed eluent (1.0 mM acetic acid, 1 mM sodium perchlorate, 5 mM cysteine, pH = 4.0) on an IonPac CS5A mixed cation-anion-exchange column. The eluting species are detected and quantified by absorbance at 210 nm.
AN43099: IC-ICP-MS speciation analysis of As in apple juice
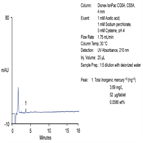
Instrument Type: ICInorganic and organic arsenic compounds have very different toxicities, and therefore speciation analysis is needed to assess the potential health risk posed by the food product. Here two inorganic and four organic arsenic species are determined in an apple juice sample using IC coupled to iCAP Q ICP-MS. Arsenic species are first separated by IC using an ammonium carbonate gradient on an IonPac AS7 column. Then the eluting species are detected and quantified by the ICP-MS down to ng/g concentrations. Arsenic speciation is also demonstrated in organic brown rice syrup (OBRS) in AN43126.
AN43098: Speciation analysis of Cr (III) and Cr (VI) in drinking waters using anion exchange chromatography coupled to ICP-MS
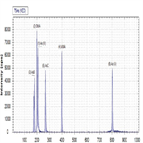
Instrument Type: ICSpeciation determinations of ionic compounds are important to determine the concentration of the more toxic form in the total elemental composition. Chromium is an industrial waste contaminant that can have serious health effects and therefore requires monitoring in municipal water systems. This method determines Chromium VI and Chromium III species in a municipal drinking water sample. The ions are separated by ion chromatography (IC) on an IonPac AG7 guard column and detected by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) at ng/g. This method is further optimized in AN43175.
AN43126: IC-ICP-MS speciation analysis of As in Organic Brown Rice Syrup (OBRS)
Instrument Type: ICInorganic and organic arsenic compounds have very different toxicities, and therefore speciation analysis is needed to assess the potential health risk posed by the food product. Here two inorganic and four organic arsenic species are determined in an Organic Brown Rice Syrup (OBRS) sample using IC coupled to ICP-MS. Arsenic species are first separated by IC using an ammonium carbonate gradient on a IonPac AS7 column. Then the eluting species are detected and quantified by the ICP-MS down to ng/g concentrations. Arsenic speciation is also demonstrated in apple juice samples (AN43099).