Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-5 of 6 results for Tag: morpholine
AN86: Determination of Trace Cations in Power Plant Waters Containing Morpholine (Method 2)
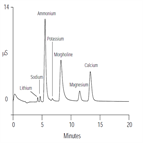
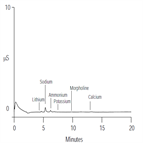
Instrument Type: ICMorpholine and ammonium are used as additives in power plant waters. Morpholine acts as a corrosion inhibitor, whereas ammonium is used to control pH. In this matrix, it is critical to determine the presence of inorganic cation contaminants. This method uses the IonPac CS14 column to quantify trace concentrations of lithium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium in the presence of high levels of ammonium and morpholine. Acetonitrile can be added to the eluent to improve peak shape and optimize resolution for some of the cations of interest.
AN86: Determination of Trace Cations in Power Plant Waters Containing Morpholine (Method 1)
Instrument Type: ICMorpholine and ammonium are used as additives in power plant waters. Morpholine acts as a corrosion inhibitor, whereas ammonium is used to control pH. In this matrix, it is critical to determine the presence of inorganic cation contaminants. This method uses the IonPac CS14 column to quantify trace concentrations of lithium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium in the presence of high levels of ammonium and morpholine. Acetonitrile can be added to the eluent to improve peak shape and optimize resolution for some of the cations of interest.
AN247 (a): Determination of Morpholine, Ethanolamine, and Hydrazine in Simulated Nuclear Power Plant Wastewater
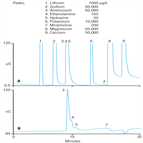
Instrument Type: ICThis Application Note describes the determination of μg/L concentrations of hydrazine, morpholine, and ethanolamine (ETA) in a simulated NPP wastewater sample containing mg/L concentrations of common cations. Morpholine and hydrazine are separated using an IonPac CS16 column with electrolytically generated methanesulfonic acid eluent. See AN 247 (b) for ETA separation on an IonPac CS15 column.
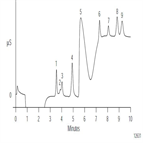
AN114: Determination of Trace Anions in High-Purity Waters Using Direct Injection and Two-Step Isocratic Ion Chromatography
Instrument Type: ICThe determination of trace anionic contamination is important to power generation and to the electronics industries to minimize corrosion. Here µg/L concentrations of anions are determined in a 1000-µL injection, in pull mode, of a morpholine solution on IonPac AS14 column. This application is optimized for a fast run time (10 min) using a two-step isocratic separation at two concentration levels of boric acid and sodium hydroxide eluents. AN114 is also suitable for trace anions in pure water. AU191 describes a similar technique to analyze samples containing boric acid and lithium.
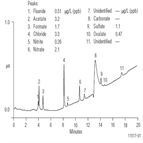
AN113: Determination of Trace Anions in High Purity Waters by High Volume/Direct Injection Ion Chromatography
Instrument Type: ICTrace anion determinations are important to the power and the electronics industries. The Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) recommends using IC to determine concentrations down to 0.25 µg/L, whereas the Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International (SEMI) recommend IC for contaminants from 0.025 to 0.5 µg/L. This application note describes the use of a gradient separation using the IonPac AS11 column for the determination of trace anions by high volume/direct injection. This method is applicable to pure water samples and high-purity waters containing corrosion inhibitors.