Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-5 of 5 results for Tag: autoneutralization
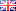
AN72481: Trace Anions by Single Pass AutoNeutralization and Ion Chromatography (IC): Anions in 5% NaOH
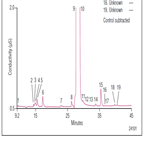
Instrument Type: ICTrace anions determinations in caustic solutions require high dilution to minimize column overload by the caustic sample. However, the high dilutions required prevent analysis of trace anionic contaminants. Here a single pass approach to neutralize the base sample is demonstrated using both suppressors run in recycle mode. The run time was reduced from 45 min in the previous version of this application, AN 93 using “Park and AutoNeutralize” to 12 min. This application is demonstrated on a 5% (w/w) sodium hydroxide sample. An ICS-6000 can be used for this application.
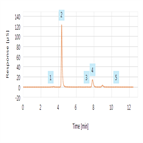
AN94: Determination of Trace Cations in Concentrated Acids (Sulfuric Acid) Using AutoNeutralization Pretreatment and Ion Chromatography
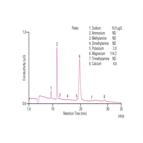
Instrument Type: ICThe determination of trace cationic contamination in processing acids (phosphoric, sulfuric, hydrofluoric) is important to the electronics industries to minimize corrosion. Here trace cationic contamination is determined in a 24% sulfuric acid sample. The acid sample is automatically neutralized through an electrolytic device, and then retained and concentrated onto a concentrator column. After eluting from the concentrator column, the µg/L cations are determined on an IonPac CS16 column using electrolytically generated MSA eluent and suppressed conductivity detection.
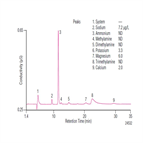
AN94: Determination of Trace Cations in Concentrated Acids (Phosphoric Acid) Using AutoNeutralization Pretreatment and Ion Chromatography
Instrument Type: ICThe determination of trace cationic contamination in processing acids (phosphoric, sulfuric, hydrofluoric) is important to the electronics industries to minimize corrosion. Here trace cationic contamination is determined in a 25% phosphoric acid sample. The acid sample is automatically neutralized through an electrolytic device, and then retained and concentrated onto a concentrator column. After eluting from the concentrator column, the µg/L cations are determined on an IonPac CS16 column using electrolytically generated MSA eluent and suppressed conductivity detection.
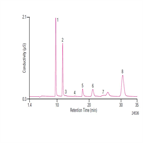
AN94: Determination of Trace Cations in Concentrated Acids (Hydrofluoric Acid) Using AutoNeutralization Pretreatment and Ion Chromatography
Instrument Type: ICThe determination of trace cationic contamination in processing acids (phosphoric, sulfuric, hydrofluoric) is important to the electronics industries to minimize corrosion. Here trace cationic contamination is determined in a 10% hydrofluoric acid sample. The acid sample is automatically neutralized through an electrolytic device, and then retained and concentrated onto a concentrator column. After eluting from the concentrator column, the µg/L cations are determined on an IonPac CS16 column using electrolytically generated MSA eluent and suppressed conductivity detection.
AU159: Determination of Volcanic Gases as Anions in Caustic Solutions Using AutoNeutralization, Automated Dilutions, and a Reagent-Free Ion Chromatography System
Instrument Type: ICThe type, amount, and ratios of volcanic gases characterize and can predict impending volcanic activity and its intensity. Changes in CO2 concentration, SO2-CO2 ratios, or halide gas composition may indicate impending volcanic eruptions. Previous analyses indicate that volcanic gases are primarily composed of CO2, water vapor, and SO2 with trace amounts of arsine and halide gases. The samples are diluted by AutoDilution to determine the major components as anions and neutralized by AutoNeutralization to determine the trace gases as anions.