Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-3 of 3 results for Tag: Physiological Fluid
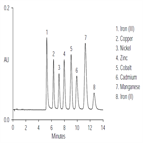
AN108:Determination of Transition Metals in Serum and Whole Blood by Ion Chromatography
Instrument Type: ICThe determination of transition metals in physiological fluids is of considerable interest in clinical chemistry. This application note describes an attractive alternative to traditional spectroscopic methods by using the principles of ion exchange. Separation between individual metals can be enhanced or altered simply by changing eluents (pyridine-2, 6-dicarboxylic acid or oxalic acid). This figure illustrates the selectivity on an IonPac CS5A column when using a pyridine-2, 6-dicarboxylic acid eluent.
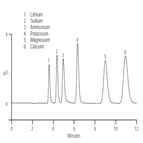
AN107: Ions (Cations) In Physiological Fluids
Instrument Type: ICOne of the most important applications of IC in clinical chemistry is the analysis of physiological fluids such as urine, plasma, and serum both for inorganic and organic anions and cations. This application note outlines the analysis of physiological fluids using ion chromatography. Here shows the cation method, the IonPac CS12A is coupled with the Cation Self-Regenerating Suppressor (CSRS) provides fast, isocratic separations of lithium, sodium, ammonium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium in less than 12 minutes using a dilute sulfuric acid eluent.
AN107: Ions (Anions) in Physiological Fluids
Instrument Type: ICOne of the most important applications of IC in clinical chemistry is the analysis of physiological fluids such as urine, plasma, and serum both for inorganic and organic anions and cations. This application note outlines the analysis of physiological fluids using ion chromatography. Part one shows the anion method, the IonPac AS11 is coupled with the Anion Self-Regenerating Suppressor (ASRS) to dramatically reduce eluent conductivity, thus allowing the use of a rapidly increasing hydroxide gradient for the separation of an extensive group of monovalent through trivalent.