Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-3 of 3 results for Tag: Microcystin
Identification and Quantitation of Microcystins by Targeted Full-Scan LC-MS/MS
Instrument Type: LCMSMSCyanobacteria, commonly referred to as blue-green algae, are photosynthetic prokaryotes that occur naturally in surface waters. They contribute significantly to primary production and nutrient cycling. Blooms of toxic cyanobacteria species in surface drinking water sources and recreational waters threaten human health. Gastrointestinal illness, skin irritation, and death following renal dialysis have been attributed to acute cyanotoxin exposure. We describe a simple and sensitive LC-MS method for definitive identification and quantitation of microcystins in water.
Analysis of Microcystins from Blue-green Algae Using the TSQ Quantum Ultra LC-MS/MS System
Instrument Type: LCMSMSOvergrowth of algae is a common problem in many wetlands with advanced stages of eutrophication (the enrichment of chemical nutrients containing nitrogen or phosphorus in an ecosystem). This often results in a thick, colored layer on the water's surface, known as an algal bloom. Some of the algae that grow in these bodies of water, known as Cyanobacteria or blue-green algae, produce toxic compounds known as microcystins. We describe a method for rapid analysis of three microcystins detected in the wetlands of Japan (Microcystin-LR, YR and RR).
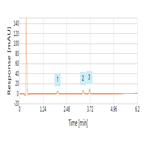
Fast separation of microcystins on a Thermo Scientific Acclaim RSLC C18 column
Instrument Type: UHPLCThe Thermo Scientific UltiMate 3000 RSLC system is applied for the analysis of microcystins. The separation is performed on a Thermo Scientific Acclaim RSLC 120 C18 2.2 µm column, with UV detection at 238 nm. While the standard method takes about an hour to run, a straightforward conversion to rapid separation LC (RSLC) using the Acclaim RSLC 120 C18 2.2 µm column shortens the analysis time to six minutes.