Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-5 of 7 results for Tag: External Water Mode
AN184: Determination of Trace Concentrations of Chlorite, Bromate, and Chlorate in Bottled Natural Mineral Waters.(Method B)
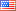
Instrument Type: ICIn this application note, we compare the Dionex IonPac AS19 using an electrolytically generated hydroxide eluent to the AS23 column using an electrolytically generated carbonate/bicarbonate eluent for the determination of chlorite, bromate, and chlorate in natural mineral waters. We compare the linearity, method detection limits, precisions, and recovery for three mineral waters obtained from three European countries to determine whether these columns have the sensitivity required to meet current EPA and EU requirements. This record describes the IonPac AS23 method.
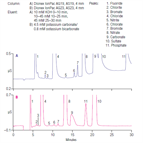
AN101: Trace Level Determination of Bromate in Ozonated Drinking Water Using Ion Chromatography.
Instrument Type: ICThis application note reports the development of a modified IC method that significantly improves the method detection limits for bromate by sample preconcentration. This method is consistent with the proposed American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) method for bromate. A weak borate eluent is used to elute the concentrated anions through the analytical column where they are separated & through the suppressed conductivity detector, they are quantified. Today we would use an approach that does not require sample preparation such as that in AN167.
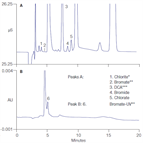
AN 136: Determination of Inorganic Oxyhalide Disinfection Byproduct Anions in Drinking Water Using IC with the Addition of a Postcolumn Reagent for Trace Bromate Analysis
Instrument Type: ICThis application note describes an improved IC method to quantify low levels of oxyhalide DBP anions and bromide in reagent water, bottled water, and finished drinking water. The method uses a Dionex IonPac AS9-HC column and suppressed conductivity detection, followed by postcolumn addition of o-dianisidine (ODA) to enhance visible absorbance detection of the bromate ion. This method allows quantification of all the key oxyhalide anions and bromide at low µg/L levels by using conductivity detection, and the postcolumn addition of ODA. Also refer to AN168 for updated method.
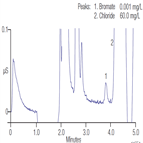
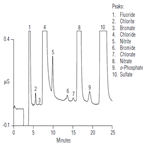
AN81: Ion Chromatographic Determination of Oxyhalides and Bromide at Trace Level Concentrations in Drinking Water Using Direct Injection.
Instrument Type: ICThis Application Note describes the use of IonPac AS9-HC column to determine trace levels of oxyhalides and bromide in the presence of common anions in drinking water, as well as their detection limits and linear concentration ranges. Unlike previous IC methods for these ions, no pretreatment cartridges are required to remove high concentrations of common ions such as chloride, bicarbonate, and sulfate. The instrumentation, techniques, and representative applications of this method are discussed in this Note. Also refer to AN167 and AN184 for updated methods.
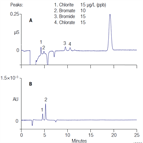
AN149: Determination of Chlorite, Bromate, Bromide, and Chlorate in Drinking Water by Ion Chromatography with an On-Line-Generated Postcolumn Reagent.
Instrument Type: ICThis application note describes an improved ion chromatography (IC) method to quantify oxyhalide DBP anions and bromide at low concentration levels in reagent water, bottled water, and finished drinking water using an approach that is technically equivalent to U.S. EPA Method 326.0. The oxyhalide anions chlorite, chlorate, bromide, and bromate are separated on a Thermo Scientific Dionex IonPac AS9-HC column and measured by using suppressed conductivity detection (as in EPA Method 300.1), followed by postcolumn reaction (PCR) to enhance detection of bromate.