Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-3 of 3 results for Tag: IonPac AS24
AN630: EPA Method 557 – Analysis of Haloacetic Acids, Dalapon, and Bromate in Drinking Water by IC-MS/MS: HAA9
Instrument Type: ICMSHaloacetic acids (HAAs) are formed as disinfection byproducts when municipal chlorination processes react with naturally occurring brominated and chlorinated species. Five HAAs are currently regulated, whereas four others may be included in future regulations. Here we demonstrate the determinations of 0.02 to 0.1 ng/L (ppt) HAA9 concentrations using ion chromatography separations combined with tandem MS on a triple quadrupole mass spectrometry.
AN201: Determination of Chloride and Sulfate in Methanol Using Ion Chromatography
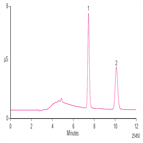
Instrument Type: ICThis application note presents a simple and direct approach for determining chloride and sulfate in methanol using a Reagent-Free™ IC system with eluent generation (RFIC-EG™ system). Chloride and sulfate are determined in less than 12 min using an IonPac® AS24 column with an electrolytically generated potassium hydroxide eluent and suppressed conductivity detection. The linearity, limits of quantitation, and precision of chloride and sulfate determination in methanol are demonstrated. This RFIC-EG system method delivers a fast and automated assay of chloride and sulfate in methanol.
AN187: Determination of Sub-µg/L Bromate in Municipal and Natural Waters
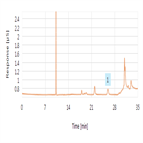
Instrument Type: ICIn this application, we demonstrate the use of a 2-D IC system to determine trace bromate concentrations in waters with high ionic strength matrices. The first dimension uses a high capacity 4-mm Thermo Scientific™ Dionex™ IonPac™ AS19 column to resolve the bromate from the matrix ions. The matrix ions are diverted to waste while a 2 mL plug is transferred to the 2-mm Thermo Scientific™ Dionex™ IonPac™ AS24 column. This method is fully automated and achieves comparable or improved sensitivity and lower cost than postcolumn addition methods.