Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-3 of 3 results for Tag: High Ionic strength water
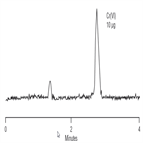
TN26: Determination of Cr(VI) in Water, Wastewater, and Solid Waste Extracts
Instrument Type: ICThe method presented here overcomes analyte interference by separating the two chromium using a detection method specific for Cr(VI) that is capable of handling the high-ionic-strength sample matrices generated in many leaching, and digestion procedures. Cr(VI) is separated as the divalent anion on the IonPac AS7 column using ammonium sulfate, ammonium hydroxide eluent. After the separation, Cr(VI) reacts with the color reagent diphenylcarbohydrazide (DPC) and detected by UV absorbance at 520 nm. This method is consistent with U.S. EPA Method 218.6. Please refer to AU179 for an updated method.
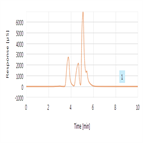
AN1116 (a) Determination of Hexavalent Chromium Cr(VI) in Drinking Water by Suppressed Conductivity Detection using Dionex IonPac AS11-HC-4µm column.
Instrument Type: ICChromates are oxyanions of chromium in the oxidation state of +6. All Cr(VI) compounds are strong oxidizing agents that are considered toxic and potentially carcinogenic. The method described here uses suppressed conductivity detection for the determination of Cr(VI) in drinking water, thus eliminating the post column derivatization used in EPA Methods 218.6 and 218.7. This new approach uses either the Dionex IonPac AS11-HC or AS11-HC-4μm column to separate chromate from other anions in HIW. Even in the challenging HIW sample, the method can easily detect and quantify 2 μg/L Cr(VI).
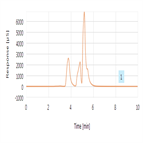
AN1116 (b) Determination of Hexavalent Chromium Cr(VI) in Drinking Water by Suppressed Conductivity Detection using the Dionex IonPac AS11-HC column.
Instrument Type: ICChromates are oxyanions of chromium in the oxidation state of +6. All Cr(VI) compounds are strong oxidizing agents that are considered toxic and potentially carcinogenic. The method described here uses suppressed conductivity detection for the determination of Cr(VI) in drinking water, thus eliminating the post column derivatization used in EPA Methods 218.6 and 218.7. This new approach uses the Dionex IonPac AS11-HC column to separate chromate from other anions in HIW. Even in the challenging HIW sample, the method can easily detect and quantify 2 μg/L Cr(VI).