Find methods for your needs
Refine by Feature
Displaying 1-5 of 8 results for Tag: Dimethylamine
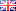
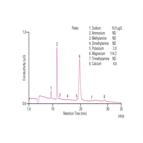
AU155: Determination of Cations and Amines in Hydrogen Peroxide by Ion Chromatography Using a RFIC (Reagent-Free) System
Instrument Type: ICHydrogen peroxide is an essential chemical in the fabrication of integrated circuit and microcircuit devices. Maximum allowable contaminate levels for semiconductor grade hydrogen peroxide can be as low as <100 ppt (ng/L) per individual inorganic cation. This application uses an IonPac CS17 column to determine trace cations and amines in hydrogen peroxide with a large-loop injection. The CS17 column separates amines without the organic solvent eluent modifier needed for separating amines when using older cation-exchange ion-chromatography (IC) columns.
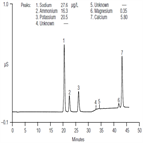
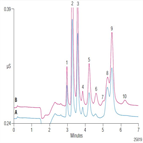
AN94: Determination of Trace Cations in Concentrated Acids (Sulfuric Acid) Using AutoNeutralization Pretreatment and Ion Chromatography
Instrument Type: ICThe determination of trace cationic contamination in processing acids (phosphoric, sulfuric, hydrofluoric) is important to the electronics industries to minimize corrosion. Here trace cationic contamination is determined in a 24% sulfuric acid sample. The acid sample is automatically neutralized through an electrolytic device, and then retained and concentrated onto a concentrator column. After eluting from the concentrator column, the µg/L cations are determined on an IonPac CS16 column using electrolytically generated MSA eluent and suppressed conductivity detection.
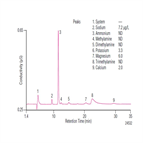
AN94: Determination of Trace Cations in Concentrated Acids (Phosphoric Acid) Using AutoNeutralization Pretreatment and Ion Chromatography
Instrument Type: ICThe determination of trace cationic contamination in processing acids (phosphoric, sulfuric, hydrofluoric) is important to the electronics industries to minimize corrosion. Here trace cationic contamination is determined in a 25% phosphoric acid sample. The acid sample is automatically neutralized through an electrolytic device, and then retained and concentrated onto a concentrator column. After eluting from the concentrator column, the µg/L cations are determined on an IonPac CS16 column using electrolytically generated MSA eluent and suppressed conductivity detection.
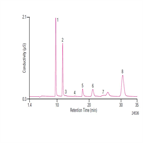
AN94: Determination of Trace Cations in Concentrated Acids (Hydrofluoric Acid) Using AutoNeutralization Pretreatment and Ion Chromatography
Instrument Type: ICThe determination of trace cationic contamination in processing acids (phosphoric, sulfuric, hydrofluoric) is important to the electronics industries to minimize corrosion. Here trace cationic contamination is determined in a 10% hydrofluoric acid sample. The acid sample is automatically neutralized through an electrolytic device, and then retained and concentrated onto a concentrator column. After eluting from the concentrator column, the µg/L cations are determined on an IonPac CS16 column using electrolytically generated MSA eluent and suppressed conductivity detection.
AN222: Determination of Parts-Per-Trillion Concentrations of Strontium by Pre-Concentration with Ion Chromatography and Suppressed Conductivity Detection
Instrument Type: ICRadioactive isotopes of strontium (90Sr and 89Sr isotopes) are byproducts of nuclear power plant reactions. 90Sr monitoring is needed because 90Sr can displace calcium in bones and teeth, resulting in long term exposure and subsequent increased cancer risk. Ion-exchange chromatography can be used to focus and isolate 90Sr from other isotopes that interfere with accurate scintillation determinations. Here ng/L of non-radioactive Sr as a retention time marker for 90Sr is pre-concentrated, then separated on an IonPac CS12A column, and detected by suppressed conductivity.